1um Flake Sphercial Graphite Powder
Flake Sphercial Graphite Powder
Specification:
| Code | C968 |
| Name | Flake Spherical Graphite Powder |
| Formula | C |
| CAS No. | 7782-42-5 |
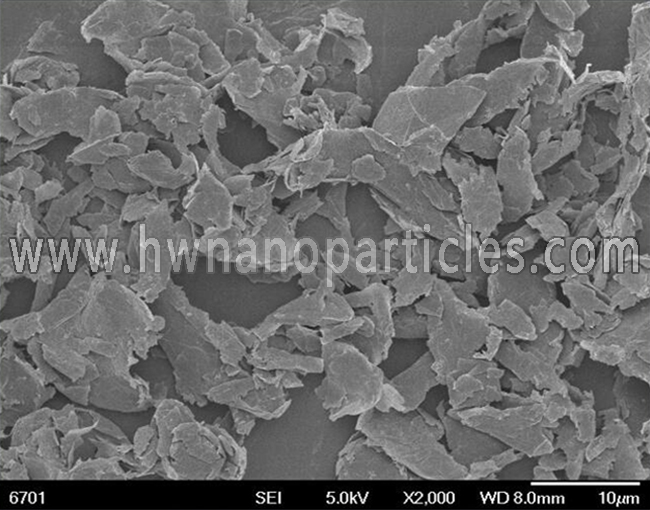
| Particle size | 1um |
| Purity | 99.95% |
| Appearance | Black powder |
| Package | 100g or as required |
| Potential applications | Coatings, refractory materials |
Description:
1. High temperature resistance: The melting point of graphite is 3850±50℃, and the boiling point is 4250℃. Even if burned by ultra-high temperature arc, the weight loss is very small, and the thermal expansion coefficient is also very small. The strength of graphite increases with the increase of temperature. At 2000°C, the strength of graphite doubles.
2. Electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity: The electrical conductivity of graphite is one hundred times higher than that of general non-metallic minerals. The thermal conductivity exceeds that of metal materials such as steel, iron, and lead. The thermal conductivity decreases with increasing temperature, and even at extremely high temperatures, graphite becomes an insulator.
3. Lubricity: The lubricating performance of graphite depends on the size of the graphite flakes. The larger the flakes, the smaller the friction coefficient and the better the lubricating performance.
4. Chemical stability: Graphite has good chemical stability at room temperature, and is resistant to acid, alkali and organic solvent corrosion.
5. Plasticity: Graphite has good toughness and can be connected into very thin sheets.
6. Thermal shock resistance: Graphite can withstand drastic changes in temperature without being damaged when used at room temperature. When the temperature changes suddenly, the volume of graphite will not change much and no cracks will occur.
Storage Condition:
Flake Spherical Graphite Powder should be well sealed, be stored in cool, dry place, avoid direct light. Room temperature storage is OK.