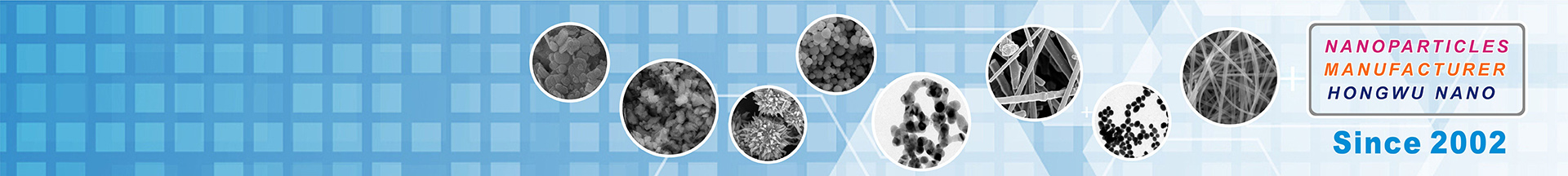
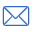
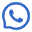
Conductive silver paste with pure conductive silver powders is a composite conductive polymer material, which is a mechanical mixture paste composed of metal conductive silver powder, base resin, solvent and additives.
Conductive silver slurry has excellent electrical conductivity and stable performance. It is one of the important basic materials in the electronic field and microelectronic technology. It is widely used in integrated circuit quartz crystal electronic components, thick film circuit surface assembly, instrumentation and other fields.
Conductive silver paste is divided into two categories:
1) Polymer silver conductive paste (baked or cured to form a film, with organic polymer as the bonding phase);
2) Sintered silver conductive paste (sintering to form a film, sintering temperature over 500℃, glass powder or oxide as the bonding phase)
The three categories of silver conductive paste require different types of silver particles or combinations as conductive fillers, and even different formulations in each category require different Ag particles as conductive functional materials. The purpose is to use the least amount of Ag powders under a certain formula or film forming process to achieve the maximum utilization of Ag’s electric and thermal conductivity, which is related to the optimization of film performance and cost.
The conductivity of the polymer is mainly determined by the conductive filler silver powder, and the amount of it is the determining factor for the conductive performance of the conductive silver paste. The influence of the content of silver powder on the volume resistivity of conductive silver paste can be given in many experiments, the conclusion is that the content of silver particle is the best in the range of 70% to 80%. The experimental results conform to the law. This is because when the silver powder content is small, the probability of particles contacting each other is small, and the conductive network is not easy to form; when the content is too large, although the probability of particle contact is high, the resin content is relatively small, and the resin connecting the silver particles is sticky, making the connection effect is correspondingly reduced, so that the chance of particles contacting each other is reduced, and the conductive network is also poor. When the filler content reaches an appropriate amount, the conductivity of the network is best to have the smallest resistivity and the largest conductivity.
Reference formula one for conductive silver paste:
Formula 1:
|
Ingredients |
Mass percentage |
Ingredient description |
|
75-82% |
Conductive filler |
|
|
Bisphenol A type epoxy resin |
8-12% |
Resin |
|
Acid anhydride curing agent |
1-3% |
Hardener |
|
Methyl imidazole |
0-1% |
Accelerator |
|
Butyl acetate |
4-6% |
Inactive diluent |
|
Active diluent 692 |
1-2% |
Active diluent |
|
Tetraethyl titanate |
0-1% |
Adhesion promoter |
|
Polyamide wax |
0-1% |
Anti-settling agent |
Conductive silver paste reference formula 2: conductive silver powder, E-44 epoxy resin, tetrahydrofuran, polyethylene glycol
Silver powder: 70%-80%
Epoxy resin: tetrahydrofuran is 1: (2-3)
Epoxy resin: curing agent is 1.0: (0.2~0.3)
Epoxy resin: polyethylene glycol is 1.00: (0.05-0.10)
High boiling point solvents: butyl anhydride acetate, diethylene glycol butyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate, isophorone
The main application of low and normal temperature curing conductive silver glue: it has the characteristics of low curing temperature, high bonding strength, stable electrical performance, and suitable for screen printing, electrical and thermal conductivity bonding in normal temperature curing welding occasions, such as quartz crystals, infrared pyroelectric detectors, piezoelectric ceramics, potentiometers, flash tubes and shielding, circuit repairs, etc.. It can also be used for conductive bonding in the radio instrumentation industry , replace solder paste to achieve conductive bonding.
The choice of curing agent is related to the curing temperature of the epoxy resin. Polyamines and polythiamines are generally used for curing at normal temperatures, while acid anhydrides and polyacids are generally used as curing agents for curing at higher temperatures. Different curing agents have different cross-linking reactions.
Dosage of curing agent: if the amount of curing agent is small, the curing time will be greatly extended or even difficult to cure; if too much curing agent, it will affect the conductivity of the silver paste and is not conducive to operation.
In the epoxy and curing agent system, how to choose a suitable diluent is related to the idea of the formula designer, such as considering: cost, dilution effect, odor, system hardness, system temperature resistance, etc.
Diluent dosage: if the diluent dosage is too small, the dissolving speed of the resin will be slow and the paste will tend to be too viscous; if the diluent dosage is too large, it is not conducive to its volatilization and the curing.
Post time: Apr-21-2021