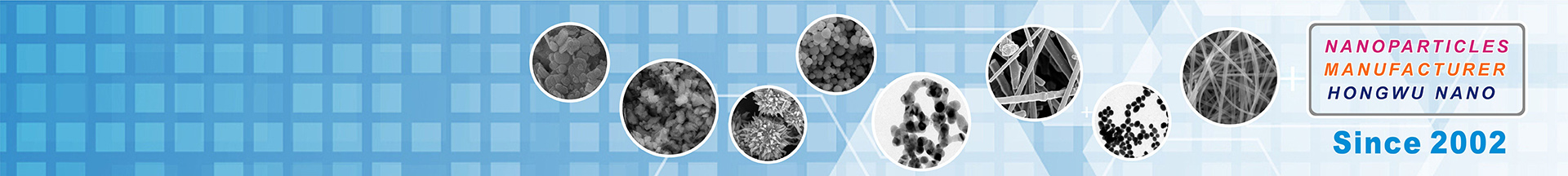
The diameter of silicon carbide nanowires is generally less than 500nm, and the length can reach hundreds of μm, which has a higher aspect ratio than silicon carbide whiskers.
Silicon carbide nanowires inherit the various mechanical properties of silicon carbide bulk materials and also have many properties unique to low-dimensional materials. Theoretically, the Young’s modulus of a single SiCNWs is about 610~660GPa; the bending strength can reach 53.4GPa, which is about twice that of SiC whiskers; the tensile strength exceeds 14GPa.
In addition, since SiC itself is an indirect bandgap semiconductor material, the electron mobility is high. Moreover, due to its nano scale size, SiC nanowires have a small size effect and can be used as a luminescent material; at the same time, SiC-NWs also show quantum effects and can be used as a semiconductor catalytic material. Nano silicon carbide wires have application potential in the fields of field emission, reinforcement and toughening materials, supercapacitors, and electromagnetic wave absorption devices.
In the field of field emission, because nano SiC wires have excellent thermal conductivity, a band gap width greater than 2.3 eV, and excellent field emission performance, they can be used in integrated circuit chips, vacuum microelectronic devices, etc.
Silicon carbide nanowires have been used as catalyst materials. With the deepening of research, they are gradually being used in photochemical catalysis. There are experiments using silicon carbide nanowires to conduct catalytic rate experiments on acetaldehyde, and compare the time of acetaldehyde decomposition using ultraviolet rays. It proves that silicon carbide nanowires have good photocatalytic properties.
Since the surface of SiC nanowires can form a large area of double-layer structure, it has excellent electrochemical energy storage performance and has been used in supercapacitors.
Post time: Dec-19-2024